Annotation
The skin, being the largest organ, performs a large number of functions. Perhaps the second most important after protective is indicator. It is by the condition of the skin that some health problems can be identified. The condition of this organ is affected by almost any process in the body - from changes in the level of certain hormones to a change in diet and even a change in environment. The most common manifestation of such changes on the skin is acne, or acne.
The rash itself can be either an external manifestation of diseases of other organs or a problem exclusively of the skin. However, when the body is healthy and the rash does not go away, its main cause will be acne.
What types of acne are there?
Blackheads (the main manifestation of acne) are inflammatory elements. They appear as a result of a complex chain of disorders: changes in the hormonal balance in the body together with the influence of external factors (insufficient or improper care, air pollution) provokes excessive production of sebum in the sebaceous glands. This secretion is a good breeding ground for P. acne bacteria, which, with their waste products, cause inflammation on the patient’s skin. In this case, the pores become clogged, which only contributes to the further development of the acne process.
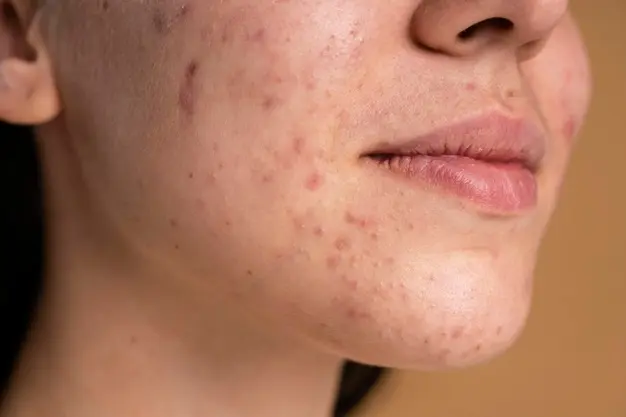
Cosmetologists classify acne rashes according to the structural features of acne:
- comedones are the simplest form, appearing as blackheads. This color is created due to the oxidation of sebum in a clogged pore;
- papular-nodular form is more typical for the second degree of acne. On the skin it looks like small nodules and pustules with a white “lid”;
- knotty form - heavier. In this case, the inflammation goes deeper, and the acne nodules reach larger sizes - often accompanied by painful sensations;
- cystic form is the most severe. In this case, the painful nodules merge, forming subcutaneous fistulas. This form requires full treatment under the supervision of a cosmetologist or dermatologist with the prescription of drug therapy.
Sometimes acne does not pose a threat and, accordingly, does not require serious treatment and goes away on its own: an example of this would be acne in newborns, acne in adolescence or after menopause.
The rash often appears where the sebaceous glands are most active: T-zone, cheeks, back, chest. In many ways, the location of acne and its severity are dictated by your skin type. So, people with oily skin type are more likely to experience these rashes - especially in the T-zone. Heredity also plays an important role in this.
What are the types of acne treatments?
If we consider acne solely as an independent skin disease, everything depends on the severity of the skin condition and the number of acne. In adults, acne more often occurs as one of the “accompanying” syndromes of diseases of other organs - in this case, a whole range of measures is needed that affect the general condition of the patient’s body along with skin treatment.
First of all, you need effective treatment of the underlying disease - this will be done by an endocrinologist, gynecologist, or gastroenterologist. In parallel with this, the cosmetologist should carry out symptomatic treatment - mainly cleaning. For nodular and cystic forms, special medications are also prescribed.
The main thing that must be ensured by treatment is a gradual impact on all links of the pathological chain, which leads to the appearance of acne on the skin. Each case is individual, but if we talk about symptomatic treatment of a skin condition, then the main action should be aimed at:
- reducing the secretion of sebaceous secretions;
- prevention of inflammation;
- prevention of scars and treatment of existing ones.
Unfortunately, this disease, even in its mildest form, requires long-term treatment, even with drugs for external use only. The key to successful therapy is patient discipline and patience. Treatment often involves changes in diet and skin care, and in some cases - daily internal medication.

Residual effects of acne - scars - can also be removed over time. If the scars remain flush with the skin (take the form of spots), the cosmetologist can lighten them over time. Hypo- and hypertrophied scars can also be treated, but it will take longer.
The main thing is to contact a dermatologist or cosmetologist in time if the rash becomes systemic. One or two inflammatory elements can be easily eliminated at home and do not indicate the presence of such a disease. If a large number of nodules or papules appear, only the recommendations of a specialist will help get rid of this problem.
Acne on the skin requires discipline - you need to follow the rules of basic care:
- cleanse and do not dry out the skin;
- remove makeup before going to bed, or even better, immediately upon returning home;
- Do not try to cleanse yourself - this will only worsen the condition of the skin and lead to scarring.
Balance is important when caring for blemish-prone skin. It needs to be moisturized, but excessive use of fatty creams can complicate the situation. It is best to use a cream selected for your skin type.
What is acne prevention?
If you know that your skin is prone to frequent rashes (oily type or close relatives have acne), the best prevention would be care prescribed by a cosmetologist.

For rare rashes in the T-zone, cosmetic cleansing will be useful. They are also recommended to be carried out during adolescence to make life easier for a teenager with this syndrome.
Children from preschool age need to be explained the rules of skin care, and in adolescence this is best done together with a cosmetologist.

















Comments
Leave your comment